
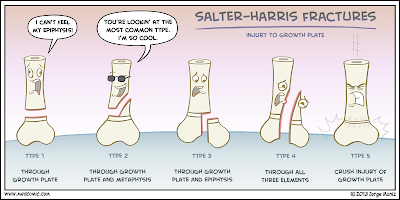
Poor prognosis as the proliferative and reserve zones are interruptedĬrushing type injury does not displace the growth plate but damages it by direct compression Salter-Harris type 2 fractures are fractures where a corner of the metaphysical bone is fractured with a displacement of the epiphysis from the metaphysic at. Poorer prognosis as the proliferative and reserve zones are interruptedįracture plane passes directly through the metaphysis, growth plate and down through the epiphysis ClassificationĬonveniently the Salter-Harris types can be remembered by the mnemonic SALTR.įracture plane passes all the way through the growth plate, not involving boneĬannot occur if the growth plate is fused citįracture passes across most of the growth plate and up through the metaphysisįracture plane passes some distance along with the growth plate and down through the epiphysis If more than 25 of the joint surface is involved or if the displacement is more than 2 to 3 mm, closed or. There are different ways to classify a growth plate fracture. Phalangeal fractures represent 3 to 7 of all physeal fractures and are usually Salter-Harris type I or type II injuries.(Kay 2001) Pediatric phalanx fractures are more common in boys than girls and are most commonly closed injuries. The patient made a satisfactory recovery with equal limb length and no evidence of. A fracture in the growth plate is known as a physeal or Salter (or Salter-Harris) fracture.
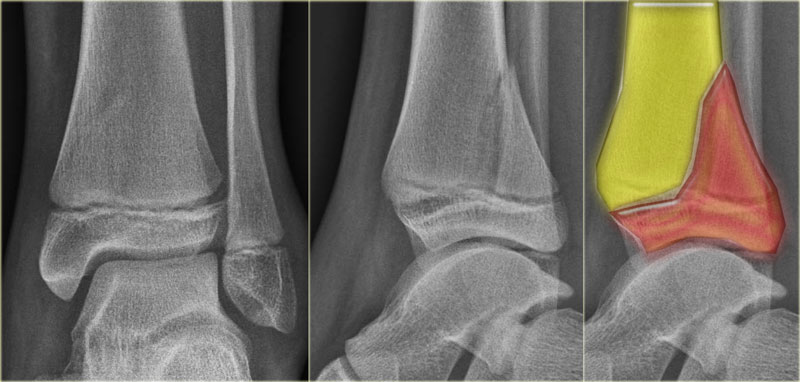
We initially managed the fatigue fracture conservatively, followed by surgical correction of the varus deformity in the knee joint. The Salter-Harris classification was proposed by Salter and Harris in 1963 1 and, at the time of writing (January 2023) remains the most widely used system for describing physeal fractures. Advanced imaging revealed a stress fracture of the left tibia with a Salter-Harris type V fracture and varus deformity of the knee.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
